
HL Paper 3
Biological pigments include a variety of chemical structures with diverse functions.
The graph shows the conversion of hemoglobin to oxyhemoglobin.
Hb(aq) + 4O2(g) Hb(O2)4(aq)
The partial pressure of oxygen gas, p(O2) is proportional to its concentration.
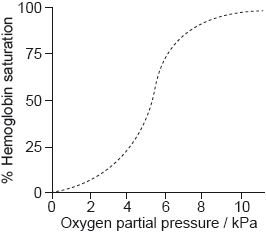
Explain the shape of the curve at low oxygen partial pressure up to about 5 kPa.
Sketch a graph on the axes above to show the effect of decreasing pH on the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin (the Bohr Effect).
Outline the effect of decreasing pH on the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin.
The structures of morphine, diamorphine and codeine are given in section 37 of the data booklet.
Methadone is used to treat heroin addiction. 1H NMR spectroscopy can be used to study its structure.
Predict the number of different hydrogen environments in the molecule ignoring the benzene rings.
Predict the chemical shift and the splitting pattern seen for the hydrogens on the carbon atom circled in the diagram. Use section 27 of the data booklet.
Ibuprofen and paracetamol are mild analgesics. One of the IR spectra below belongs to ibuprofen and the other to paracetamol. The structures of both compounds are given in section 37 of the data booklet.
Both spectra show a peak at wavenumber 1700 cm–1. Identify the bond responsible for this peak.
Deduce which spectrum belongs to paracetamol, giving two reasons for your choice. Use section 26 of the data booklet.
Describe how mild analgesics function.
Physical properties of elements vary according to atomic number. Sections 6 to 9 of the data
booklet list some of these properties.
Melting points and boiling points of elements 1 to 95
Deduce, giving a reason, the group of elements in the periodic table most likely to undergo sublimation.
Describe the density trend across periods 4 and 5 of the periodic table.
Suggest, with a reason, whether the lanthanoids or actinoids of the f-block would have the higher density.
Compare the ease of oxidation of s-block and d-block metals to their melting points and densities. Use section 25 of the data booklet.
Sketch how the first ionization energies of elements vary with their atomic radius.
Bromine and methanoic acid react in aqueous solution.
Br2 (aq) + HCOOH (aq) → 2Br− (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + CO2 (g)
The reaction was monitored by measuring the volume of carbon dioxide produced as time
progressed.
Determine from the graph the rate of reaction at 20 s, in cm3 s−1, showing your working.
Outline, with a reason, another property that could be monitored to measure the rate of this reaction.
Describe one systematic error associated with the use of the gas syringe, and how the error affects the calculated rate.
Identify one error associated with the use of an accurate stopwatch.
Aspirin is one of the most widely used drugs in the world.
Aspirin was synthesized from 2.65 g of salicylic acid (2-hydroxybenzoic acid) (Mr = 138.13) and 2.51 g of ethanoic anhydride (Mr = 102.10).
Suggest two absorbances, other than the absorbances due to the ring structure and C–H bonds, that would be present in the infrared (IR) spectrum of aspirin.
State two techniques, other than IR spectroscopy, which could be used to confirm the identity of aspirin.
Alloys containing at least 60 % copper reduce the presence of bacteria on their surface.The percentage of copper in brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, can be determined by UV-vis spectrometry.
A sample of brass is dissolved in concentrated nitric acid and then made up to 250.0 cm3 with water before analysis.
Cu (s) + 4HNO3 (aq) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2NO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
3Zn (s) + 8HNO3 (aq) → 3Zn(NO3)2 (aq) + 2NO (g) + 4H2O (l)
The concentration of copper(II) ions in the resulting solution is then determined from a calibration curve, which is plotted by measuring the light absorbance of standard solutions.
You may find the following chart and diagram helpful.
Outline why the initial reaction should be carried out under a fume hood.
Deduce the equation for the relationship between absorbance and concentration.
Copper(II) ion solutions are blue. Suggest, giving your reason, a suitable wavelength of light for the analysis.
Outline how a solution of 0.0100 mol dm−3 is obtained from a standard 1.000 mol dm−3 copper(II) sulfate solution, including two essential pieces of glassware you would need.
The original piece of brass weighed 0.200 g. The absorbance was 0.32.
Calculate, showing your working, the percentage of copper by mass in the brass.
Deduce the appropriate number of significant figures for your answer in (e)(i).
Comment on the suitability of using brass of this composition for door handles in hospitals.
If you did not obtain an answer to (e)(i), use 70 % but this is not the correct answer.
Suggest another property of brass that makes it suitable for door handles.
Titration is another method for analysing the solution obtained from adding brass to nitric acid.
Copper(II) ions are reduced to copper(I) iodide by the addition of potassium iodide solution, releasing iodine that can be titrated with sodium thiosulfate solution, Na2S2O3 (aq). Copper(I) iodide is a white solid.
4I− (aq) + 2Cu2+ (aq) → 2CuI (s) + I2 (aq)
I2 (aq) + 2S2O32− (aq) → 2I− (aq) + S4O62− (aq)
Suggest why the end point of the titration is difficult to determine, even with the addition of starch to turn the remaining free iodine black.
Solubility plays an important role in the bioavailability of drugs in the body.
Suggest why aspirin is slightly soluble in water. Refer to section 37 of the data booklet.
A student prepares aspirin from salicylic acid in the laboratory, extracts it from the reaction mixture, ensures the sample is dry and determines its melting point.
Suggest why the melting point of the student’s sample is lower and not sharp compared to that of pure aspirin.
Organic molecules can be characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
Compare and contrast the infrared peaks above 1500 cm−1 in pure samples of aspirin and salicylic acid using section 26 of the data booklet.
Some mild analgesics contain a solid mixture of acidic aspirin and a non-acidic organic chemical of similar polarity to asprin.
Discuss how acid-base properties and the process of solvent extraction can be used to separate aspirin from the mixture.
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the largest producers of waste solvents.
State a green solution to the problem of organic solvent waste.
Polymers have a wide variety of uses but their disposal can be problematic.
Draw a section of isotactic polychloroethene (polyvinylchloride, PVC) showing all the atoms and all the bonds of four monomer units.
The infrared (IR) spectrum of polyethene is given.
Suggest how the IR spectrum of polychloroethene would diff er, using section 26 of the data booklet.
Explain how plasticizers affect the properties of plastics.
Suggest why the addition of plasticizers is controversial.
Outline, giving a reason, how addition and condensation polymerization compare with regard to green chemistry.
Draw the full structural formula of the organic functional group formed during the polymerization of the two reactants below.
Changes in physiology can impact living creatures.
The graph shows the change in oxygen partial pressure in blood, measured at different pH values.
Explain the effect of changing pH on the percentage saturation of hemoglobin at a given partial pressure of oxygen.
Explain the biomagnification of the pesticide DDT.
Vitamins are organic compounds essential in small amounts.
State the name of one functional group common to all three vitamins shown in section 35 of the data booklet.